Your local photographer
Passport Photo Maker [+Expert Verification]
Time-saving, efficient, and stress-free—that’s how taking ID photos with our passport photo tool is! Try it now and experience the convenience of pictures done from home.


![Passport Photo Maker [+Expert Verification]](https://passport-photo.online/images/cms/after_image_3bf0612bd7.webp?quality=80&format=webp&width=1080)
![Passport Photo Maker [+Expert Verification]](https://passport-photo.online/images/cms/before_image_941bc6609c.webp?quality=80&format=webp&width=1080)

As seen in








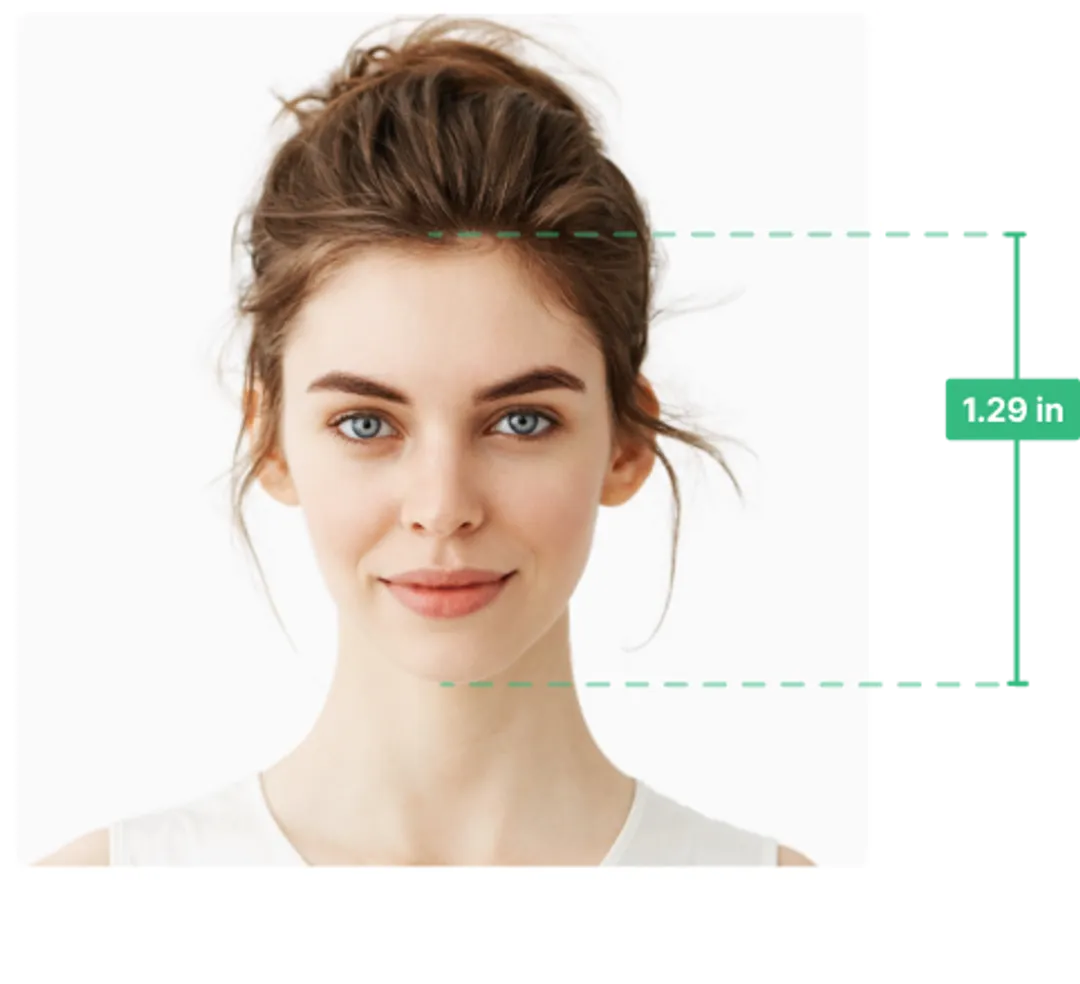
US Passport Size Photo Requirements
Your photo must meet specific criteria set by the US government for passport photos.






Mateusz is a seasoned specialist in biometric photography with over 5 years of hands-on experience. As a member of the prestigious British Institute of Professional Photography (BIPP) and the Association of Photographers (AOP), he has helped thousands of clients worldwide capture compliant photos for official documents.
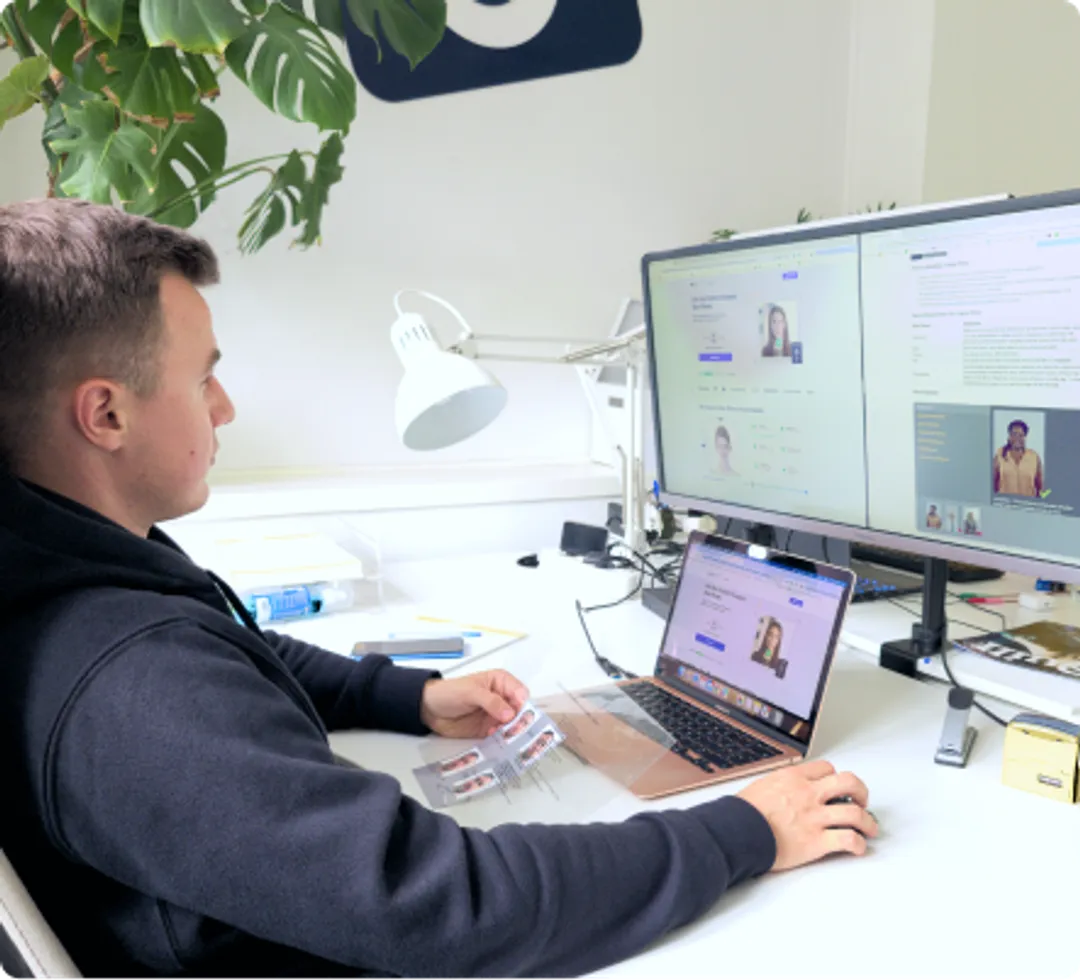
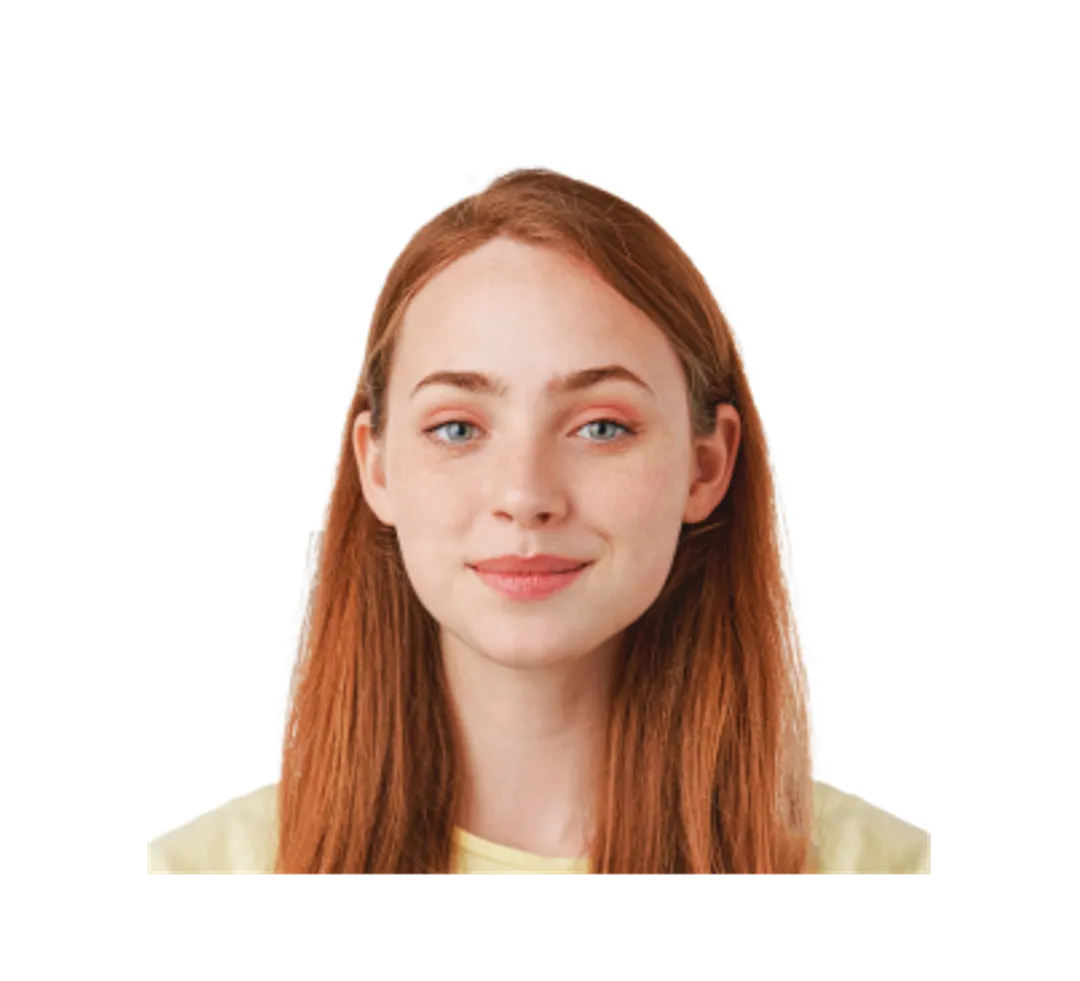


















You'll receive a perfectly sized digital photo, which you can attach to an online application for your first passport or a passport renewal.
Our passport photo generator creates a 4x6-inch template, perfect for printing passport photos at home or at any popular store.
Our local print shops produce high-quality photo prints and deliver them to you.
Estimated delivery 2-3 business days

You'll receive a perfectly sized digital photo, which you can attach to an online application for your first passport or a passport renewal.
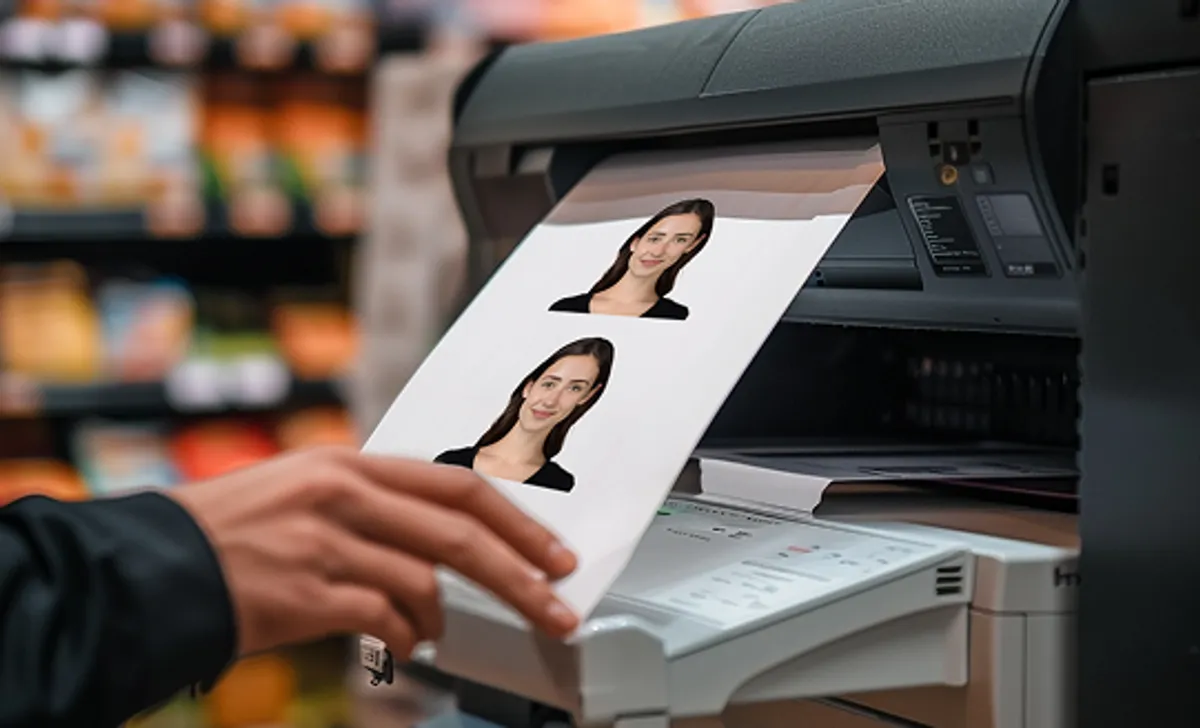

Our passport photo generator creates a 4x6-inch template, perfect for printing passport photos at home or at any popular store.
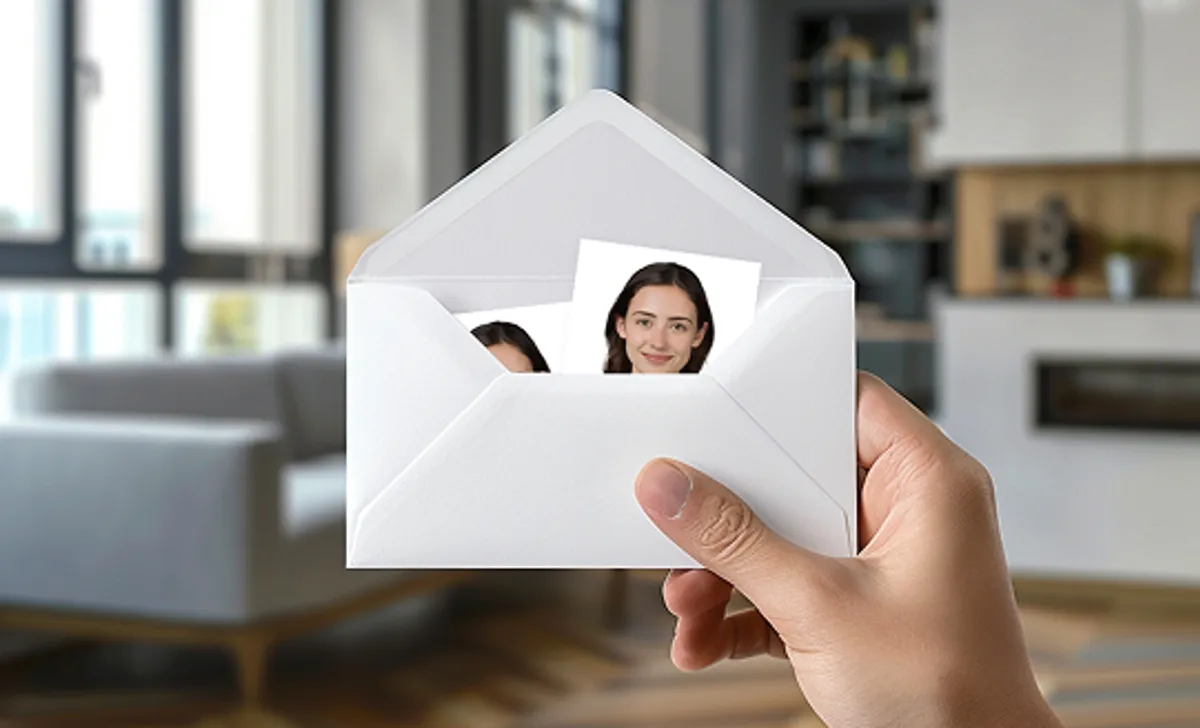

Our local print shops produce high-quality photo prints and deliver them to you.
Estimated delivery 2-3 business days
Discover where to get passport photos in the comparison table below and see why we excel.
Best deal | |||
|---|---|---|---|
 |  Other tools or DYI | ||
Choose your best shot | |||
 Printed photos | At home, at store or delivered from us | From the photographer | At home or at a store |
 Compliance guarantee | |||
 Skills needed | No skills required | No skills required | Photo editing, photography |
 Equipment needed | Smartphone | Travel to the photo shop | Good camera, white wall, photo editing software |
Al compliance check | |||
 Human expert compliance check | |||
 Time | 1 min | 30 min (+travel time) | 4 hours |
More People Now Use an Online Passport Photo Editor

over 2.2 million photos taken online!
See What Our Customers Say about Us
This is a superb service
This is a superb service. I ordered & then realised I needed hard copy photos instead. I got onto their support who were incredibly fast & efficient. They sent me the link & made it so easy & effortless. The photos arrived very quickly. I HIGHLY RECOMMEND them.
Great
Great, simple and easy. Photos accepted by the passport office
Quick service
I needed to get a passport photo after business hours when all the stores were closed. In a pinch, I was able to upload a selfie and the site edited it for me with a white background and sent me the image file by email within 10 minutes. It was great because I received an electronic file for quick upload and a printable version with two pictures side by side.
It was exactly what I needed!
This is a superb service
This is a superb service. I ordered & then realised I needed hard copy photos instead. I got onto their support who were incredibly fast & efficient. They sent me the link & made it so easy & effortless. The photos arrived very quickly. I HIGHLY RECOMMEND them.
Great
Great, simple and easy. Photos accepted by the passport office
Quick service
I needed to get a passport photo after business hours when all the stores were closed. In a pinch, I was able to upload a selfie and the site edited it for me with a white background and sent me the image file by email within 10 minutes. It was great because I received an electronic file for quick upload and a printable version with two pictures side by side.
It was exactly what I needed!
This is a superb service
This is a superb service. I ordered & then realised I needed hard copy photos instead. I got onto their support who were incredibly fast & efficient. They sent me the link & made it so easy & effortless. The photos arrived very quickly. I HIGHLY RECOMMEND them.
Great
Great, simple and easy. Photos accepted by the passport office
Quick service
I needed to get a passport photo after business hours when all the stores were closed. In a pinch, I was able to upload a selfie and the site edited it for me with a white background and sent me the image file by email within 10 minutes. It was great because I received an electronic file for quick upload and a printable version with two pictures side by side.
It was exactly what I needed!


Mateusz is a seasoned specialist in biometric photography with over 5 years of hands-on experience. As a member of the prestigious British Institute of Professional Photography (BIPP) and the Association of Photographers (AOP), he has helped thousands of clients worldwide capture compliant photos for official documents.
Our experts are available 24/7 to assist with your photo.


Mateusz is a seasoned specialist in biometric photography with over 5 years of hands-on experience. As a member of the prestigious British Institute of Professional Photography (BIPP) and the Association of Photographers (AOP), he has helped thousands of clients worldwide capture compliant photos for official documents.
Our experts are available 24/7 to assist with your photo.


Roxana is a writer with 3+ years of experience. As a Master in psycholinguistics, she blends her passion for language and communication with insights from diverse cultures, making her content resonate with a broad audience.
Our experts are available 24/7 to assist with your photo.


Karolina, a licensed legal advisor with a Master of Law, specializes in passport photo compliance, ensuring adherence to international standards set by the US Department of State and ICAO. Combining her legal expertise and technical knowledge, she excels in navigating complex global regulations with meticulous attention to detail and a firm grasp of international law.
Our experts are available 24/7 to assist with your photo.


Simon Wojtyczka is a writer with experience living and working in 7 countries, each adding depth to his work. Holding a Master's in Applied Linguistics, he has a profound grasp of language and its intricate ties to culture.
Our experts are available 24/7 to assist with your photo.


Sylwia is a skilled writer with a BA in English Studies and an active SPJ member. For nearly three years now, she's been writing captivating articles for international companies, turning her lifelong passion into a career.
Our experts are available 24/7 to assist with your photo.


Jess is a passport photo specialist and a member of the British Institute of Professional Photography (BIPP). She has reviewed over 400,000 passport photos, making sure they meet strict global standards. With a sharp eye for detail and extensive knowledge of international photo regulations, Jess helps clients get compliant photos every time.
Our experts are available 24/7 to assist with your photo.
Why We’re like No Other Passport Photo Maker
of photos are reviewed by our experts within one minute of purchase.
of our customers receive a compliant photo within 15 minutes of placing an order.
photos are processed daily by our passport generator on average.

One of our qualified experts will manually review your submitted photo to ensure it meets official requirements. If something is off, we'll help you to fix the issue at no extra cost.
Roxana is a writer with 3+ years of experience. As a Master in psycholinguistics, she blends her passion for language and communication with insights from diverse cultures, making her content resonate with a broad audience.
Mateusz is a seasoned specialist in biometric photography with over 5 years of hands-on experience. As a member of the prestigious British Institute of Professional Photography (BIPP) and the Association of Photographers (AOP), he has helped thousands of clients worldwide capture compliant photos for official documents.
Passport Photo Maker—All You Need to Know
Making appointments, traveling to the passport office, or waiting in lines are now a thing of the past. Let us introduce you to Passport Photo Online—your professional pocket-size passport photo tool.
Thanks to this passport photo maker, you can prepare photos in a matter of minutes from home. And they’re just a click away—all work is on our side. Read on to discover more!
How to use our passport photo tool
Our passport photo generator is available for you as a web-based platform or a passport photo app for Android or iOS. The steps for getting your passport photo with us are exactly the same. Follow these instructions to ensure you’ll end up with a 100% compliant photo.
Step #1: Provide us with a photo
Whether you decide to use our website or a mobile app, you must provide us with a proper photo. You don’t have to worry about the background—just find a well-lit spot and take a picture with a smartphone or a digital camera. Remember you need to keep your head straight and have a neutral facial expression.

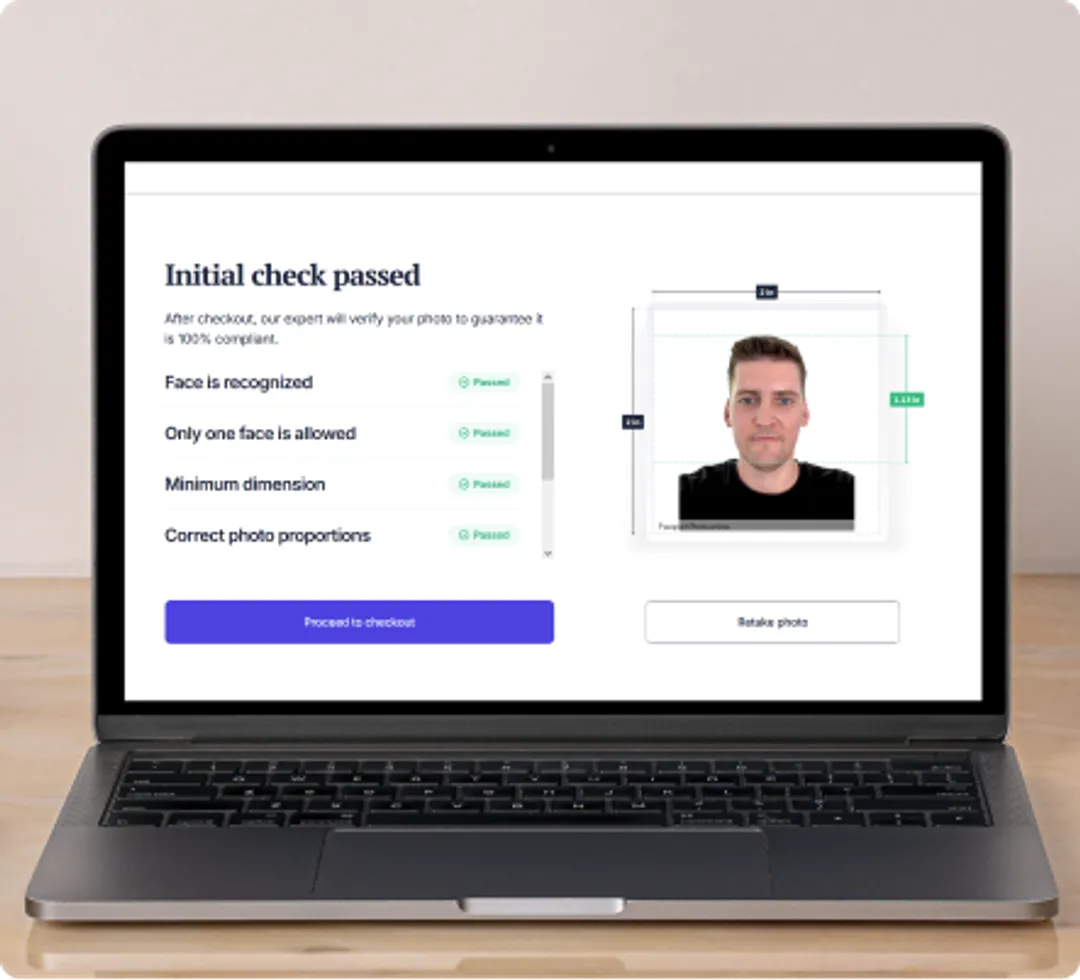
Step #2: Go through the initial check
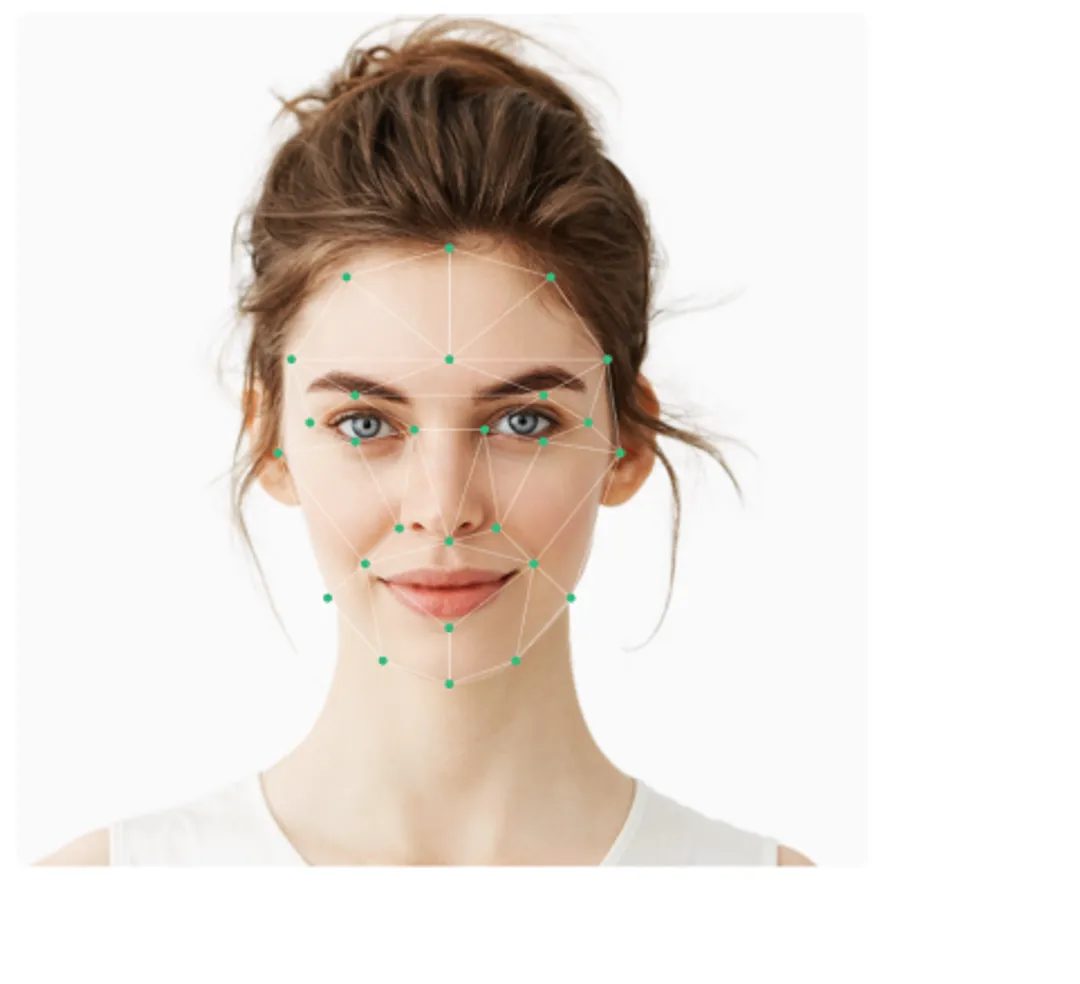
Your photo is automatically checked by our advanced AI technology. It ensures that your image has proper dimensions (after cropping and resizing it to your desired document), your face is recognizable, and you’re the only person in the picture.
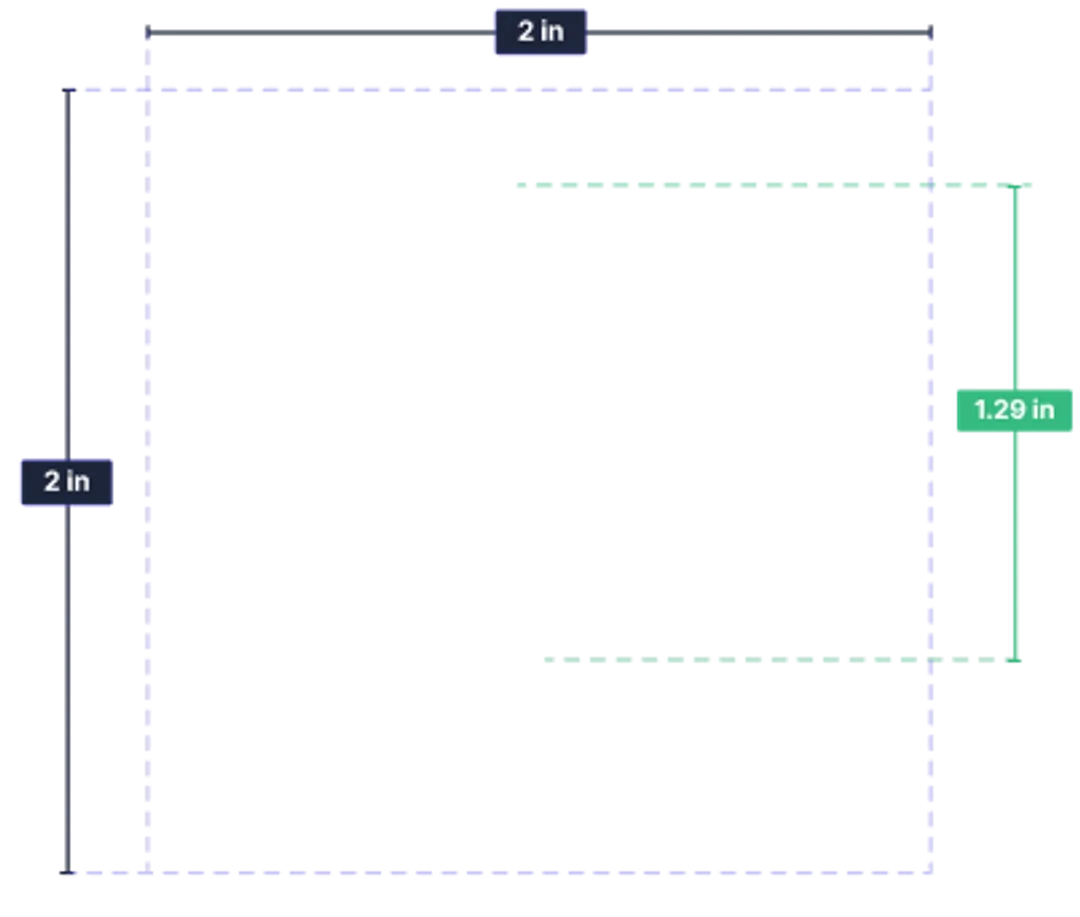
The initial check will also show you the proper passport photo size—follow them (especially the head size) if your photo happens to be rejected at this point. You can retake your picture as many times as you want!

Step #3: Go through the checkout
If you’re happy with the result, proceed to checkout—there, you’ll have a choice between a digital passport image (and a ready-to-print template) or printed high-quality photos delivered to your door within 2–3 business days (for free).
A digital passport photo costs $16.95. Please note that if you choose “printed” in your checkout, you’ll receive a digital image at its full price AND two printed passport pictures for only $3.00. That way, you’ll pay $19.95 in total.
You’ll receive your digital passport photo immediately after processing the payment. We’ll send it to you along with a 4x6-inch template to print on your email address. And you’ll receive your passport photo printouts at your door in up to 3 business days.
Note: If you need more than two photos, you can choose the option of four photos ($2.50 extra) or six photos ($4.00 extra).

Step #4: Wait until our expert verifies your photo
We want to ensure that your passport picture meets all official requirements. That’s why it also goes through an expert review process. If some of your picture’s elements are missing or not in line with the regulations, we’ll inform you about that. You can then retake your photo for free, and we’ll repeat the same process.
Our photo experts carefully review every photograph taken with our passport photo tool. In the unfortunate case of your photo being rejected by the authorities, we guarantee a 200% refund.
Step #5: Your perfect passport photos are on the way!
And there it is—a perfect photo for your passport is ready for delivery!
You can enjoy the results immediately with a digital image sent to your inbox. It’s ready for any online application, but if you need the paper one, your high-quality passport photo printouts are only 3 business days away!
We sincerely hope that our passport photo tool meets your expectations!

Benefits of using our passport size photo maker
As you can see, using Passport Photo Online is as easy as 1-2-3. But what’s hiding behind your perfect passport pictures? Let us show you how many features are compiled within this one passport photo tool.
The passport photo online process was easy to follow, and I was surprised at how quickly my photo was reviewed to meet all requirements and then available to me for downloading.
Tamara (US)
Passport size photo converter
First of all, you can transform any picture—within the official regulations—into a passport photo. You can take a photo in your garden (but be careful about the shadows), in your living room, or your office. Then, our passport photo tool will crop and resize your photograph so that it fits the requirements of your chosen document.
Passport photo editor
While it’s forbidden to enhance or alter your passport photo in any way, you can still edit your photo and retake it as many times as you need. Thanks to our passport photo tool, it’s possible to preview your picture and decide if you need another snapshot.
Passport photo background remover
No more worries about a perfectly white background—you don’t need to look for a white wall or place a white sheet behind you anymore. Our passport photo editor will remove any background and replace it with a white or off-white one as per the requirements.
Passport photo template generator
Prefer to print passport photos on your own? We’ve got you covered! Together with your digital passport image, you’ll receive a printable image on a 4x6-inch template. Remember to use high-quality photo paper for your passport photographs.
You can take the template and print the picture at one of the popular pharmacies or retail stores for cents.
Pocket-size passport photo booth
Best of all—you can create your own photo studio wherever you are. Fancy staying at home? Snap a photo! Staying abroad and in need of a passport renewal? Snap a photo! Need a passport for your newborn? Snap a photo in a cozy, comfortable space!
Whatever the circumstances, Passport Photo Online is here to help you achieve the best passport photo results.

Sources:
https://www.trustpilot.com/review/passport-photo.online
https://tsg.phototool.state.gov/photo
https://travel.state.gov/content/travel/en/passports/how-apply/photos.html
Documents
We provide photos for IDs from all over the world. You’ll find the one you are looking for!

Popular Documents
Popular Documents Around the World
Related documents

FAQ

Take a photo conveniently from home and use our passport photo resizer—your picture will be automatically cropped and converted to the correct size.
While there are many photo tools available, most require manual work from your side. Try Passport Photo Online, enjoy the all-automatized experience, and receive your 2x2 passport photos in the blink of an eye!
You can use free photo editor software to get a 2x2 picture. However, mostly they don’t offer background removal or compliance checks. Try Passport Photo Online—for a fair price, you’ll receive a digital image, two 2x2 passport photo printouts, automatic photo editing, and a 100% compliance guarantee (plus a 200% refund in a rare case of rejection).

Are You Satisfied With Our Service?
Let us know how we’re doing.
Customer feedback is always welcome.
Rate Your Reading Experience:





Rating: 4.79/5
Number of votes: 4762































